When it comes to treating heart disease, one of the most important decisions patients face is whether to opt for bypass surgery vs angioplasty. Both procedures are designed to treat blockages in the coronary arteries, but they work in different ways and are used for different types of heart conditions. The decision between these two treatment options can be difficult, and many factors come into play when making this choice. Let’s explore the differences between bypass surgery and angioplasty, what you should consider, and how to determine the best option for your specific condition.
NOTE: Choosing between bypass surgery vs angioplasty is a significant decision, and it’s important to consider the severity of your heart disease, your overall health, recovery time, and the long-term effectiveness of the procedure. Both options offer benefits, and your healthcare provider will work with you to determine the most appropriate treatment for your condition. Remember that, with proper care and lifestyle changes, heart disease can be managed effectively, and both procedures can help restore quality of life.
Understanding Bypass Surgery and Angioplasty
What Is Bypass Surgery?
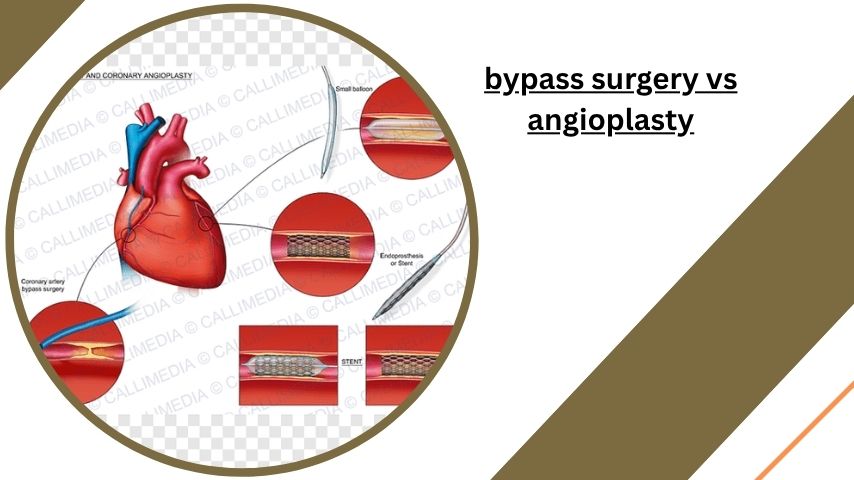
Bypass surgery is a major surgical procedure where a surgeon creates new pathways (bypasses) for blood to flow around blocked arteries. In this procedure, the surgeon uses healthy blood vessels from other parts of the body (often the leg, arm, or chest) to reroute blood around the blocked or narrowed arteries. This restores proper blood flow to the heart muscle, improving its function.
Bypass surgery is often recommended for patients with severe coronary artery disease (CAD), especially when there are multiple blockages in the heart’s arteries or if angioplasty is not an option.
What Is Angioplasty?
Angioplasty, also known as percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), is a minimally invasive procedure used to open narrowed or blocked coronary arteries. In this procedure, a small balloon is inserted into the blocked artery and inflated to widen the artery. Often, a stent (a small mesh tube) is also placed to keep the artery open. Angioplasty is typically recommended for patients with one or two blockages, especially if the blockages are in specific areas of the arteries.
Angioplasty is a less invasive procedure than bypass surgery, often allowing for a faster recovery time. It can be done on an outpatient basis, meaning patients can go home the same day.
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Bypass Surgery vs Angioplasty
1. Severity of Blockages
The most important factor in deciding between bypass surgery vs angioplasty is the severity of the blockages in the arteries. If the blockages are widespread or involve multiple major arteries, bypass surgery may be the better choice. This is especially true if the arteries are severely narrowed or if there is a risk that angioplasty would not be effective in the long term.
On the other hand, angioplasty is usually sufficient for patients with less severe blockages in one or two arteries. It is a good option when the blockages are in smaller branches of the coronary arteries and can be safely treated with balloon dilation and stent placement.
2. Your Overall Health and Medical History
Your overall health and medical history will also play a significant role in the decision. Bypass surgery is a more invasive procedure, and as such, it carries higher risks, particularly for older patients or those with other health issues, such as diabetes or kidney disease. If you have a history of heart disease or other serious medical conditions, your doctor may recommend angioplasty as a safer alternative.
3. Recovery Time and Post-Procedure Care
Angioplasty is a less invasive procedure and typically requires a shorter recovery time. Most patients are able to resume normal activities within a few days to a week. On the other hand, bypass surgery is a more complex procedure, and recovery may take several weeks to months. Patients who undergo bypass surgery often need to stay in the hospital for a few days and may require follow-up care, including physical therapy, to regain strength.
If a faster recovery time is important to you, angioplasty may be the preferred option, provided it’s suitable for your condition.
4. Long-Term Effectiveness
Both bypass surgery and angioplasty are effective in treating coronary artery disease, but their long-term outcomes can differ. Angioplasty is often effective at restoring blood flow in the short term, but the arteries may become narrowed again over time, a condition known as restenosis. In some cases, another angioplasty may be needed.
Bypass surgery, on the other hand, provides a more long-term solution, as it creates a new pathway for blood to flow around the blocked arteries. While the grafts used in bypass surgery can also become blocked over time, the success rate for bypass surgery tends to be higher in patients with severe heart disease.
5. Cost and Insurance Coverage
The cost of both bypass surgery vs angioplasty can vary significantly. Bypass surgery is a more expensive procedure due to the need for anesthesia, a longer hospital stay, and more intensive post-operative care. Angioplasty, being minimally invasive, tends to be less expensive and may be covered under most health insurance plans with lower out-of-pocket costs.
However, the cost should not be the sole deciding factor, as the right procedure will depend on the severity of your condition and your long-term heart health needs.
Bypass Surgery vs Angioplasty: Which Is Right for You?
The decision between bypass surgery vs angioplasty depends on many factors, including the severity of your heart disease, your overall health, and your doctor’s recommendations. While angioplasty is a great option for some patients, others may benefit more from the long-term benefits of bypass surgery. Your healthcare provider will consider these factors and guide you toward the treatment that best suits your needs.
Other Considerations in Heart Health
In addition to bypass surgery vs angioplasty, there are other important factors to consider when making decisions about your heart health. For example, if you have other health issues, such as needing tooth extraction vs root canal or knee replacement surgery, these may affect your recovery process or the type of heart treatment you receive. Your doctor will consider your complete medical history and any other procedures you may need in the future when determining the best course of action.
Conclusion
If you are facing heart disease and need to make this important decision, consult with your cardiologist to discuss the best treatment plan for your unique situation.
Don’t wait to make an informed decision about your heart health. Speak with a trusted healthcare provider today and explore whether bypass surgery vs angioplasty is the right option for you. Get the expert advice and personalized care you deserve—schedule a consultation now!
For more insightful articles related to this topic, feel free to visit getbacklinkseo
